 |
 | |
| Species: |
Rat |
| Strain/breeder: |
CRL:WI (GLX/BRL/HAN)/ CR |
| Sex: |
Male/Female |
| Age: |
78 days |
| Study type: |
OECD 407, 4 weeks |
| Treatment: |
6-Propyl-2-thiouracil/High dose group |
| Animal status: |
Sacrified |
| Clinical findings: |
|
| Organ(s): |
Thyroid gland |
Macroscopic
finding(s): |
Enlargement of thyroid glands |
| Staining: |
H&E |
|
 |
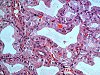
Fig. 1 (99k)
|
|
Abstract
Effect of propylthiouracil (PTU) on thyroid glands in rats
J. WALTER
BASF AG, Department of Product Safety, Regulations, Toxicology and Ecology, GV/T, Z470, 67056 Ludwigshafen, Germany
Key words: thyroid glands, rat, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, PTU
Reduced serum thyroid hormone concentrations of T3/T4 and the consequential increase in serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) have been proposed to mediate the stimulation and growth of the thyroid glands.
In an enhanced OECD 407 type study, rats were fed with propylthiouracil (PTU) at dose levels of 0.1, 1.0, and 10 mg/kg/day by gavage for 4 weeks. In the high dose group rats, serum T3 was reduced by 72% in males and by 70% in females , T4 was reduced by 84% in males and by 78% in females. TSH was increased by 902% in males and by 1107% in females in high dose group animals. The weight of the thyroid gland was increased by 650% in males and by 637% in females in the high dose group. Histologically there was an associated severe hypertrophy and hyperplasia of follicular cells. A thorough histopathology examination with standard H&E slides is sufficient to evaluate substances causing such effects on the thyroid glands.
case index | << previous case | next case >>
|
 |